Glove products
ECG vs EMG Disposable Electrodes: Key Differences in Design and Function
In the human body, everything operates through a complex network of electrical signals. These enable coordination and regulation in higher order for various essential activities. To understand such complex processes, doctors make use of electrophysiological tests as diagnostic tools. Among them, ECG and EMG studies are two of the most important techniques that assess heart and muscle activities. Central to both techniques are specialized electrodes that play a vital interfacing role in transmitting the body’s electrical signals to diagnostic equipment.
The article presents a comparison between disposable ECG and EMG electrodes based on design, material composition, and the critical considerations involved in effectively capturing data for diagnostic purposes while ensuring comfort for the patient.
ECG Electrodes: Unveiling the Heart’s Electrical Symphony
Electrocardiography, relying on the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases, allows the recording of electrical activity of the heart and provides important information about its rhythm, conduction, and possible abnormalities.
ECG Electrodes Placement: Cartography of the Cardiac Landscape
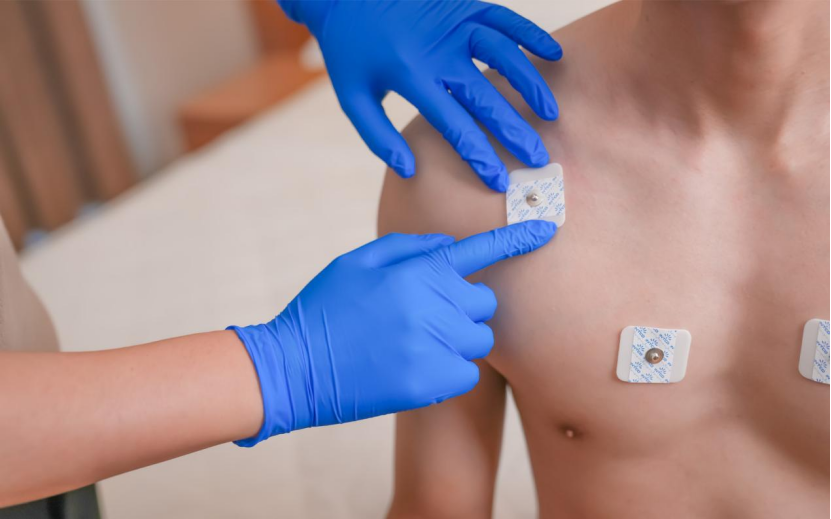
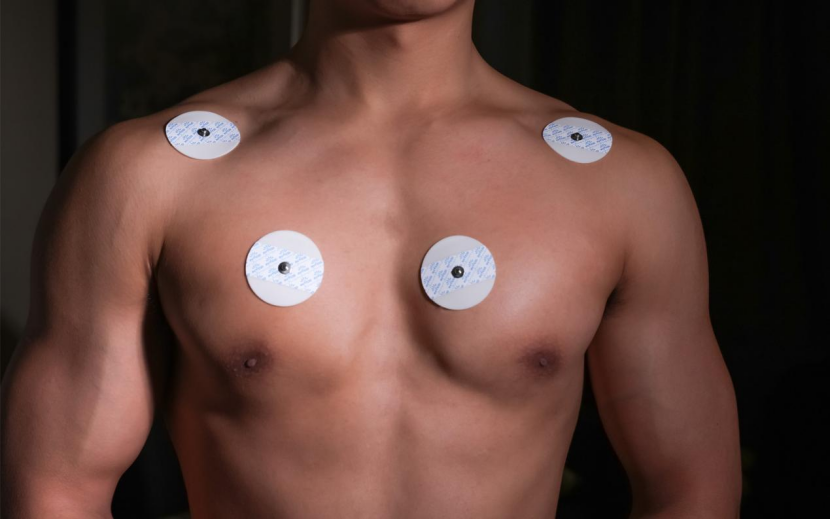
ECG electrodes are placed on the body in such a way that they can capture comprehensive electrical activity from different perspectives. The most common configuration is the 12-lead ECG, which requires 10 electrodes to be placed on the body as follows:
-Chest (Precordial Leads):V1-V6
-Limbs (Limb Leads):RA, LA, RL, LL
This provides many electrical viewpoints of the heart and allows healthcare professionals to evaluate its function from multiple angles.
ECG Electrodes Material Composition: Balancing Conductivity, Adhesion, and Comfort
Disposable ECG electrodes are designed with multiple layers, each optimized for performance:
-Conductive Gel:This usually consists of a silver/silver chloride Ag/AgCl layer, which provides the critical bridge in the transmission of electrical signals, hence allowing for stable conductivity.
-Adhesive Layer: This ensures the electrode stays attached during monitoring, providing a secure connection resistant to movement or sweat, while skin irritation is minimal.
-Backing Material: Materials like foam, non-woven fabric, or micropore paper provide support and breathability to prevent gel leakage and enhance comfort during long-term wear.
ECG Electrodes Design Considerations: Optimizing Signal Acquisition and Patient Experience
The design of ECG electrodes is a trade-off between signal quality and comfort for the patient. The main considerations are as follows:
-Size and Shape of Electrode:Smaller electrodes may pick up weaker signals, while larger electrodes provide stronger signals but are uncomfortable.
-Adhesive Strength: Strong adhesives are used for secure placement, but the material should not be too aggressive to cause skin irritation.
-Gel Composition:Preferred is Ag/AgCl gel for its high conductivity and hypoallergenic properties that minimize skin reactions.
-Breathability:Breathability prevents skin maceration during long-term monitoring, especially with micropore paper and foam electrodes.
EMG Electrodes: Unraveling Muscle Whispers
Electromyography (EMG) focuses on recording the electrical activity generated by muscle fibers. Disposable EMG electrodes are essential in capturing subtle muscle signals, enabling accurate assessments of muscle function and the detection of neuromuscular disorders.
EMG Electrodes Placement: Pinpointing Neuromuscular Junctions
EMG electrodes can be used either on the skin’s surface or directly in the muscle:
-Surface EMG: Non-invasive electrodes are placed on the skin over target muscles, useful for general muscle assessments and detecting gross abnormalities.
–Needle EMG:Invasive electrodes inserted directly into muscle tissue provide a more localized and precise measurement of muscle fiber activity, especially useful for diagnosing specific neuromuscular disorders.
EMG Electrodes Material Composition: Balancing Signal Fidelity and Minimizing Invasive Impact
Materials for the manufacture of electrodes are a subject of an explicit balance between the quality of the output signal and personal discomfort, which applies most strongly when talking about needle electrodes:
-Needle Electrodes:Fine needles commonly manufactured from stainless steel or platinum and sometimes Teflon-coated record individual muscle fiber activity. The gauge and design of the needle affect both the precision in signal acquisition and patient comfort.
-Surface Electrodes:Surface electrodes are like ECG electrodes but with conductive gels, adhesive, and sometimes stronger adhesives that can keep good contact during muscle contractions.
Comparing ECG and EMG Disposable Electrodes: A Head-to-Head Comparison
While both ECG and EMG electrodes are indispensable in diagnosis, their design, intended use, and material composition are worlds apart because of the two different signal characteristics that emanate from the heart and muscles.
|
Feature |
ECG Electrodes |
EMG Electrodes |
|
Purpose |
Monitoring heart activity |
Assessing muscle activity |
|
Placement |
Skin surface (chest, limbs, back) |
Skin surface (surface EMG) or directly into muscle (needle EMG) |
|
Material Composition |
Conductive gel (Ag/AgCl), adhesive, backing material (foam, fabric, paper) |
Needle electrodes (stainless steel, platinum, Teflon coated), surface electrodes (similar to ECG electrodes, potentially stronger adhesives) |
|
Design Considerations |
Signal clarity, adhesion, comfort, breathability |
Signal specificity, patient tolerance (needle electrodes), stability, signal amplification |
INTCO Medical: Leading the Way in Electrode Design
INTCO Medical has a vast product portfolio of all categories. It gives priority to medical consumables, healthcare equipment, and physiotherapy care products. The uses of its products can be extended to medical institutions, elderly care facilities, homes, and industries concerning safety. INTCO Medical’s wide range of electrodes also includes:
-INTCO MedicalFoam ECG Electrodes: INTCO Medical Foam ECG Electrodes are made of medical-grade foam with AG/AGCl sensors, suitable for both short- and long-term monitoring in ICU and anesthesia.
-INTCO MedicalDisposable Non-woven ECG Electrodes: Gentle, breathable electrodes for long-term monitoring up to 72 hours, recommended for sensitive skin and in ICU cases.
-INTCO MedicalDisposable Micropore ECG Electrodes: Soft and breathable, used on sensitive skin.
-INTCO MedicalMedical Tape ECG Electrodes: For sensitive skin, made of breathable tape; these are usually used during stress tests and Holter monitoring.
The Importance of Specialized Electrode Designs
The differences between ECG and EMG disposable electrodes reflect the distinct nature of the electrical signals they are designed to capture. INTCO Medical, a leading global manufacturer of disposable medical supplies, understands the critical role that high-quality, reliable products play in accurate diagnoses and positive patient experiences.